在某些情况下,出于隐私或安全原因,您可能需要防止记录跟踪的输入和输出。LangSmith 提供了一种在将跟踪的输入和输出发送到 LangSmith 后端之前过滤它们的方法。
如果您想完全隐藏跟踪的输入和输出,可以在运行应用程序时设置以下环境变量:
LANGSMITH_HIDE_INPUTS=true
LANGSMITH_HIDE_OUTPUTS=true
Client 实例自定义和覆盖此行为。这可以通过在 Client 对象上设置 hide_inputs 和 hide_outputs 参数(TypeScript 中为 hideInputs 和 hideOutputs)来完成。
对于下面的示例,我们将为 hide_inputs 和 hide_outputs 简单地返回一个空对象,但您可以根据需要自定义此内容。
import openai
from langsmith import Client
from langsmith.wrappers import wrap_openai
openai_client = wrap_openai(openai.Client())
langsmith_client = Client(
hide_inputs=lambda inputs: {}, hide_outputs=lambda outputs: {}
)
# The trace produced will have its metadata present, but the inputs will be hidden
openai_client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4o-mini",
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant."},
{"role": "user", "content": "Hello!"},
],
langsmith_extra={"client": langsmith_client},
)
# The trace produced will not have hidden inputs and outputs
openai_client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4o-mini",
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant."},
{"role": "user", "content": "Hello!"},
],
)
基于规则的输入和输出掩码
此功能在以下 LangSmith SDK 版本中可用:
- Python:0.1.81 及更高版本
- TypeScript:0.1.33 及更高版本
create_anonymizer / createAnonymizer 函数,并在实例化客户端时传递新创建的匿名器。匿名器可以从正则表达式模式列表和替换值构造,也可以从接受并返回字符串值的函数构造。
如果 LANGSMITH_HIDE_INPUTS = true,将跳过输入的匿名器。如果 LANGSMITH_HIDE_OUTPUTS = true,输出也是如此。
但是,如果要将输入或输出发送到客户端,anonymizer 方法将优先于在 hide_inputs 和 hide_outputs 中找到的函数。默认情况下,create_anonymizer 只会查看最多 10 个嵌套级别深度,这可以通过 max_depth 参数配置。
from langsmith.anonymizer import create_anonymizer
from langsmith import Client, traceable
import re
# create anonymizer from list of regex patterns and replacement values
anonymizer = create_anonymizer([
{ "pattern": r"[a-zA-Z0-9._%+-]+@[a-zA-Z0-9.-]+.[a-zA-Z]{2,}", "replace": "<email-address>" },
{ "pattern": r"[0-9a-fA-F]{8}-[0-9a-fA-F]{4}-[0-9a-fA-F]{4}-[0-9a-fA-F]{4}-[0-9a-fA-F]{12}", "replace": "<UUID>" }
])
# or create anonymizer from a function
email_pattern = re.compile(r"[a-zA-Z0-9._%+-]+@[a-zA-Z0-9.-]+.[a-zA-Z]{2,}")
uuid_pattern = re.compile(r"[0-9a-fA-F]{8}-[0-9a-fA-F]{4}-[0-9a-fA-F]{4}-[0-9a-fA-F]{4}-[0-9a-fA-F]{12}")
anonymizer = create_anonymizer(
lambda text: email_pattern.sub("<email-address>", uuid_pattern.sub("<UUID>", text))
)
client = Client(anonymizer=anonymizer)
@traceable(client=client)
def main(inputs: dict) -> dict:
...
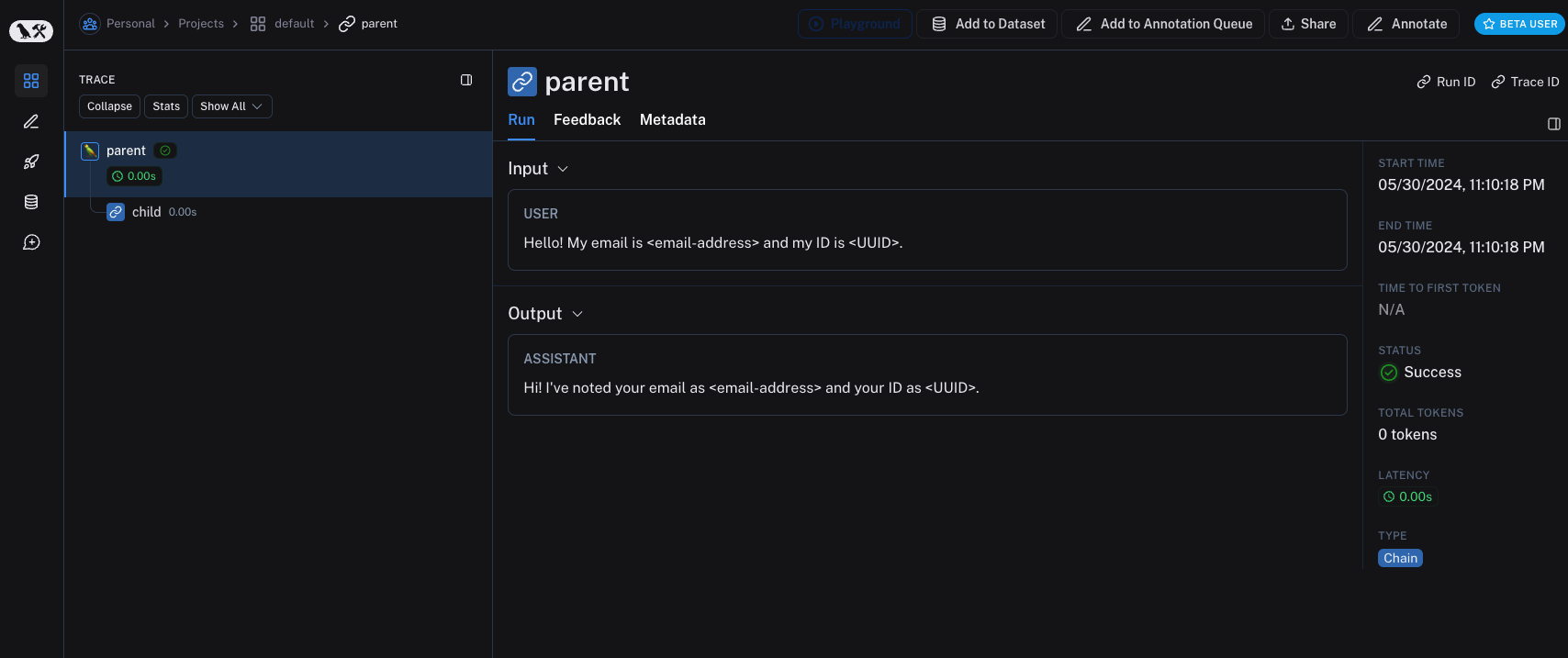 较旧版本的 LangSmith SDK 可以使用
较旧版本的 LangSmith SDK 可以使用 hide_inputs 和 hide_outputs 参数来实现相同的效果。您还可以使用这些参数更有效地处理输入和输出。
import re
from langsmith import Client, traceable
# Define the regex patterns for email addresses and UUIDs
EMAIL_REGEX = r"[a-zA-Z0-9._%+-]+@[a-zA-Z0-9.-]+.[a-zA-Z]{2,}"
UUID_REGEX = r"[0-9a-fA-F]{8}-[0-9a-fA-F]{4}-[0-9a-fA-F]{4}-[0-9a-fA-F]{4}-[0-9a-fA-F]{12}"
def replace_sensitive_data(data, depth=10):
if depth == 0:
return data
if isinstance(data, dict):
return {k: replace_sensitive_data(v, depth-1) for k, v in data.items()}
elif isinstance(data, list):
return [replace_sensitive_data(item, depth-1) for item in data]
elif isinstance(data, str):
data = re.sub(EMAIL_REGEX, "<email-address>", data)
data = re.sub(UUID_REGEX, "<UUID>", data)
return data
else:
return data
client = Client(
hide_inputs=lambda inputs: replace_sensitive_data(inputs),
hide_outputs=lambda outputs: replace_sensitive_data(outputs)
)
inputs = {"role": "user", "content": "Hello! My email is user@example.com and my ID is 123e4567-e89b-12d3-a456-426614174000."}
outputs = {"role": "assistant", "content": "Hi! I've noted your email as user@example.com and your ID as 123e4567-e89b-12d3-a456-426614174000."}
@traceable(client=client)
def child(inputs: dict) -> dict:
return outputs
@traceable(client=client)
def parent(inputs: dict) -> dict:
child_outputs = child(inputs)
return child_outputs
parent(inputs)
The process_outputs parameter is available in LangSmith SDK version 0.1.98 and above for Python.
process_inputs and process_outputs parameters of the @traceable decorator.
These parameters accept functions that allow you to transform the inputs and outputs of a specific function before they are logged to LangSmith. This is useful for reducing payload size, removing sensitive information, or customizing how an object should be serialized and represented in LangSmith for a particular function.
Here’s an example of how to use process_inputs and process_outputs:
from langsmith import traceable
def process_inputs(inputs: dict) -> dict:
# inputs is a dictionary where keys are argument names and values are the provided arguments
# Return a new dictionary with processed inputs
return {
"processed_key": inputs.get("my_cool_key", "default"),
"length": len(inputs.get("my_cool_key", ""))
}
def process_outputs(output: Any) -> dict:
# output is the direct return value of the function
# Transform the output into a dictionary
# In this case, "output" will be an integer
return {"processed_output": str(output)}
@traceable(process_inputs=process_inputs, process_outputs=process_outputs)
def my_function(my_cool_key: str) -> int:
# Function implementation
return len(my_cool_key)
result = my_function("example")
process_inputs creates a new dictionary with processed input data, and process_outputs transforms the output into a specific format before logging to LangSmith.
It’s recommended to avoid mutating the source objects in the processor functions. Instead, create and return new objects with the processed data.
@traceable(process_inputs=process_inputs, process_outputs=process_outputs)
async def async_function(key: str) -> int:
# Async implementation
return len(key)
hide_inputs and hide_outputs) when both are defined.
Quick starts
You can combine rule-based masking with various anonymizers to scrub sensitive information from inputs and outputs. In this how-to-guide, we’ll cover working with regex, Microsoft Presidio, and Amazon Comprehend.
Regex
The implementation below is not exhaustive and may miss some formats or edge cases. Test any implementation thoroughly before using it in production.
import re
import openai
from langsmith import Client
from langsmith.wrappers import wrap_openai
# Define regex patterns for various PII
SSN_PATTERN = re.compile(r'\b\d{3}-\d{2}-\d{4}\b')
CREDIT_CARD_PATTERN = re.compile(r'\b(?:\d[ -]*?){13,16}\b')
EMAIL_PATTERN = re.compile(r'\b[A-Za-z0-9._%+-]+@[A-Za-z0-9.-]+\.[A-Z|a-z]{2,7}\b')
PHONE_PATTERN = re.compile(r'\b(?:\+?1[-.\s]?)?\(?\d{3}\)?[-.\s]?\d{3}[-.\s]?\d{4}\b')
FULL_NAME_PATTERN = re.compile(r'\b([A-Z][a-z]*\s[A-Z][a-z]*)\b')
def regex_anonymize(text):
"""
Anonymize sensitive information in the text using regex patterns.
Args:
text (str): The input text to be anonymized.
Returns:
str: The anonymized text.
"""
# Replace sensitive information with placeholders
text = SSN_PATTERN.sub('[REDACTED SSN]', text)
text = CREDIT_CARD_PATTERN.sub('[REDACTED CREDIT CARD]', text)
text = EMAIL_PATTERN.sub('[REDACTED EMAIL]', text)
text = PHONE_PATTERN.sub('[REDACTED PHONE]', text)
text = FULL_NAME_PATTERN.sub('[REDACTED NAME]', text)
return text
def recursive_anonymize(data, depth=10):
"""
Recursively traverse the data structure and anonymize sensitive information.
Args:
data (any): The input data to be anonymized.
depth (int): The current recursion depth to prevent excessive recursion.
Returns:
any: The anonymized data.
"""
if depth == 0:
return data
if isinstance(data, dict):
anonymized_dict = {}
for k, v in data.items():
anonymized_value = recursive_anonymize(v, depth - 1)
anonymized_dict[k] = anonymized_value
return anonymized_dict
elif isinstance(data, list):
anonymized_list = []
for item in data:
anonymized_item = recursive_anonymize(item, depth - 1)
anonymized_list.append(anonymized_item)
return anonymized_list
elif isinstance(data, str):
anonymized_data = regex_anonymize(data)
return anonymized_data
else:
return data
openai_client = wrap_openai(openai.Client())
# Initialize the LangSmith client with the anonymization functions
langsmith_client = Client(
hide_inputs=recursive_anonymize, hide_outputs=recursive_anonymize
)
# The trace produced will have its metadata present, but the inputs and outputs will be anonymized
response_with_anonymization = openai_client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4o-mini",
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant."},
{"role": "user", "content": "My name is John Doe, my SSN is 123-45-6789, my credit card number is 4111 1111 1111 1111, my email is john.doe@example.com, and my phone number is (123) 456-7890."},
],
langsmith_extra={"client": langsmith_client},
)
# The trace produced will not have anonymized inputs and outputs
response_without_anonymization = openai_client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4o-mini",
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant."},
{"role": "user", "content": "My name is John Doe, my SSN is 123-45-6789, my credit card number is 4111 1111 1111 1111, my email is john.doe@example.com, and my phone number is (123) 456-7890."},
],
)
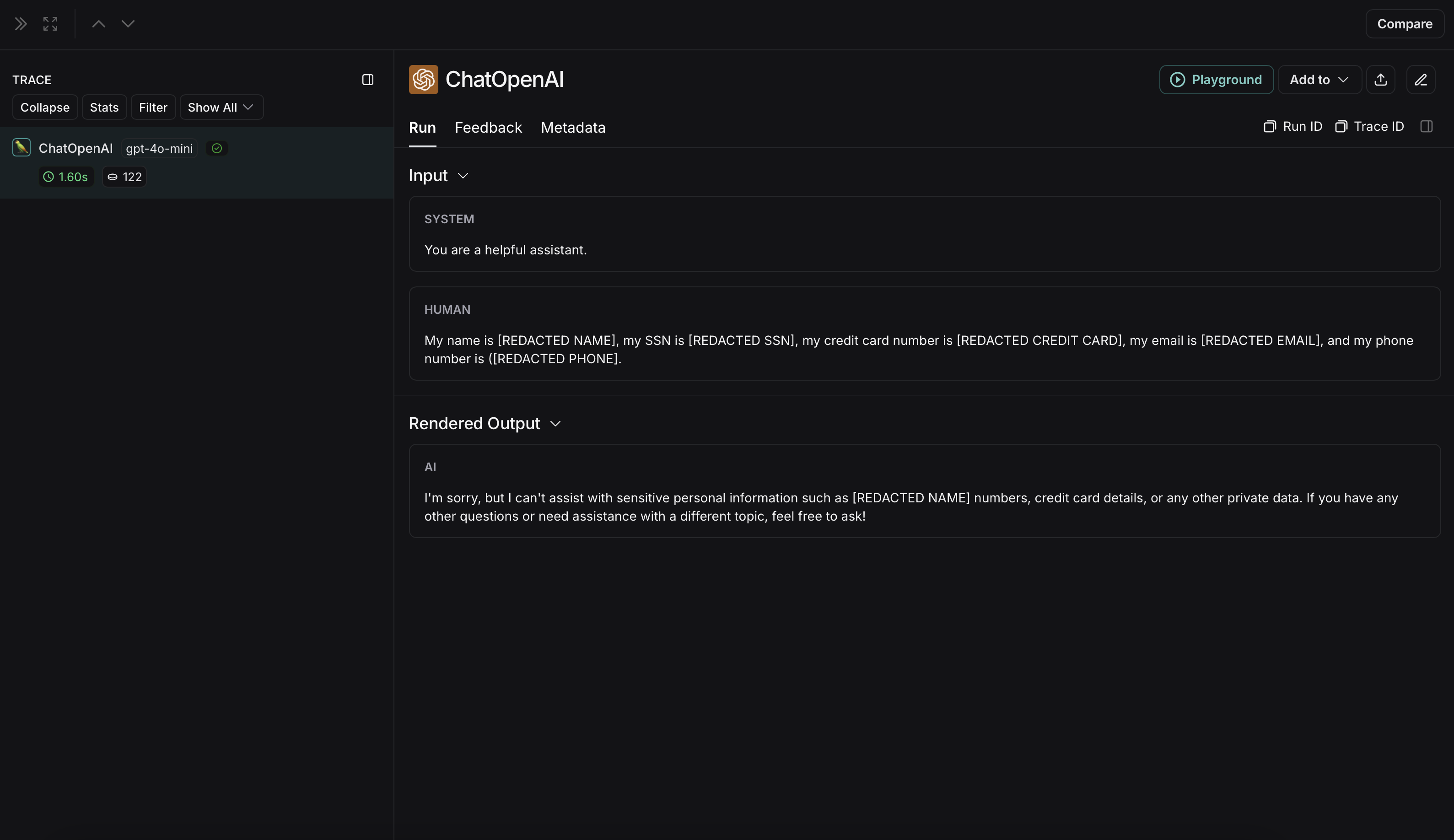 The non-anonymized run will look like this in LangSmith:
The non-anonymized run will look like this in LangSmith: 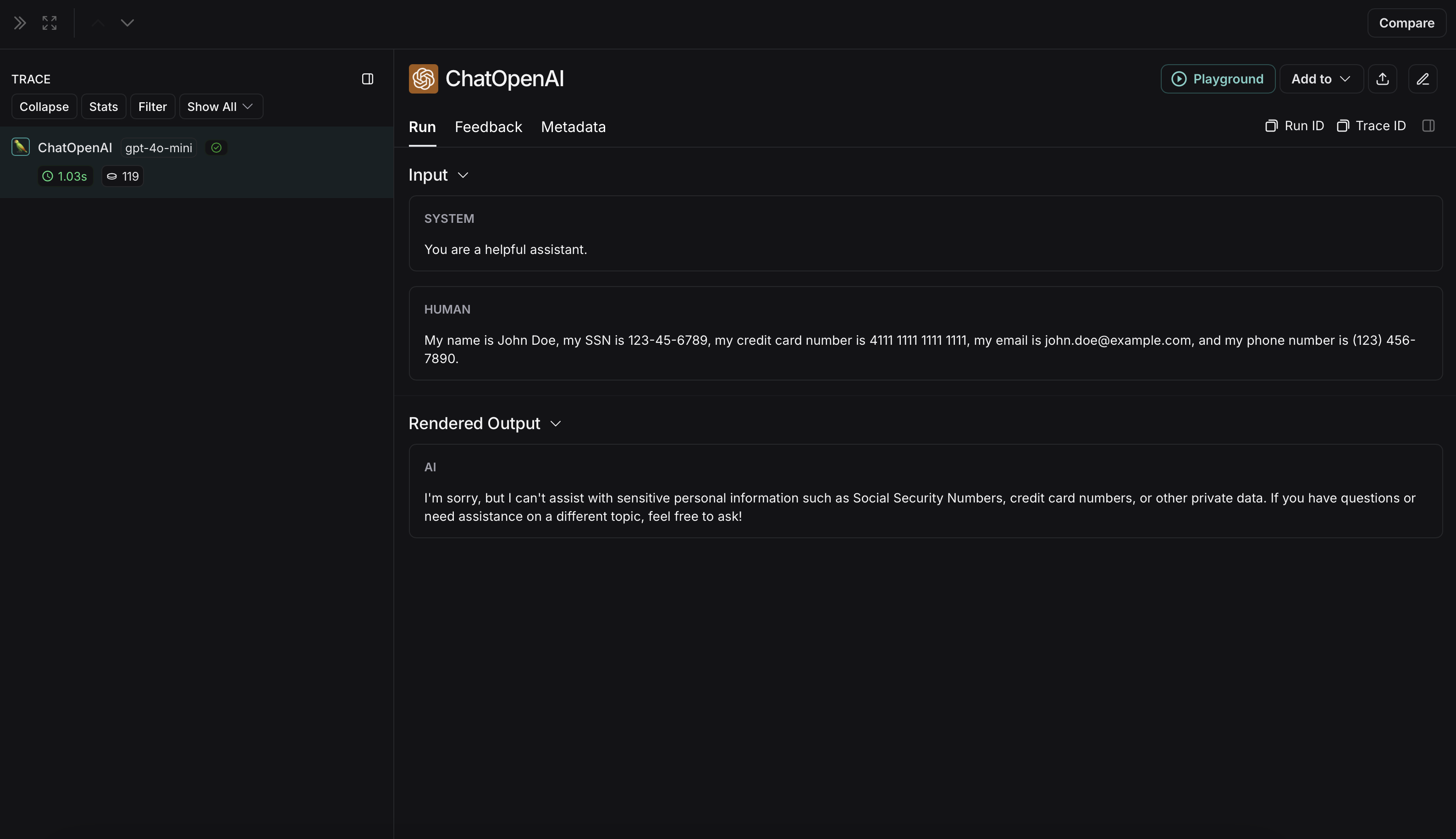
Microsoft Presidio
The implementation below provides a general example of how to anonymize sensitive information in messages exchanged between a user and an LLM. It is not exhaustive and does not account for all cases. Test any implementation thoroughly before using it in production.
pip install presidio-analyzer
pip install presidio-anonymizer
python -m spacy download en_core_web_lg
import openai
from langsmith import Client
from langsmith.wrappers import wrap_openai
from presidio_anonymizer import AnonymizerEngine
from presidio_analyzer import AnalyzerEngine
anonymizer = AnonymizerEngine()
analyzer = AnalyzerEngine()
def presidio_anonymize(data):
"""
Anonymize sensitive information sent by the user or returned by the model.
Args:
data (any): The data to be anonymized.
Returns:
any: The anonymized data.
"""
message_list = (
data.get('messages') or [data.get('choices', [{}])[0].get('message')]
)
if not message_list or not all(isinstance(msg, dict) and msg for msg in message_list):
return data
for message in message_list:
content = message.get('content', '')
if not content.strip():
print("Empty content detected. Skipping anonymization.")
continue
results = analyzer.analyze(
text=content,
entities=["PERSON", "PHONE_NUMBER", "EMAIL_ADDRESS", "US_SSN"],
language='en'
)
anonymized_result = anonymizer.anonymize(
text=content,
analyzer_results=results
)
message['content'] = anonymized_result.text
return data
openai_client = wrap_openai(openai.Client())
# initialize the langsmith client with the anonymization functions
langsmith_client = Client(
hide_inputs=presidio_anonymize, hide_outputs=presidio_anonymize
)
# The trace produced will have its metadata present, but the inputs and outputs will be anonymized
response_with_anonymization = openai_client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4o-mini",
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant."},
{"role": "user", "content": "My name is Slim Shady, call me at 313-666-7440 or email me at real.slim.shady@gmail.com"},
],
langsmith_extra={"client": langsmith_client},
)
# The trace produced will not have anonymized inputs and outputs
response_without_anonymization = openai_client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4o-mini",
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant."},
{"role": "user", "content": "My name is Slim Shady, call me at 313-666-7440 or email me at real.slim.shady@gmail.com"},
],
)
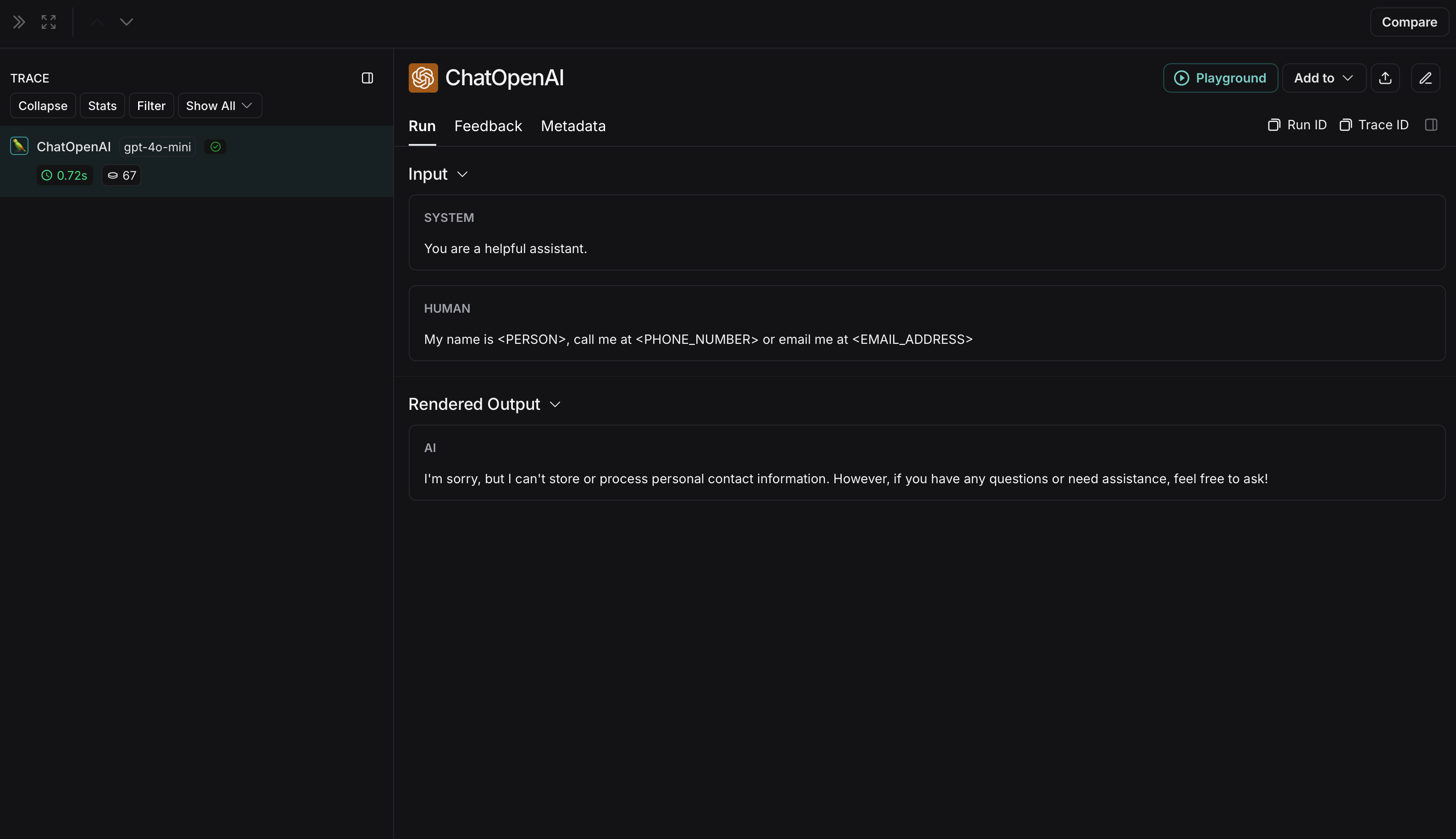 The non-anonymized run will look like this in LangSmith:
The non-anonymized run will look like this in LangSmith: 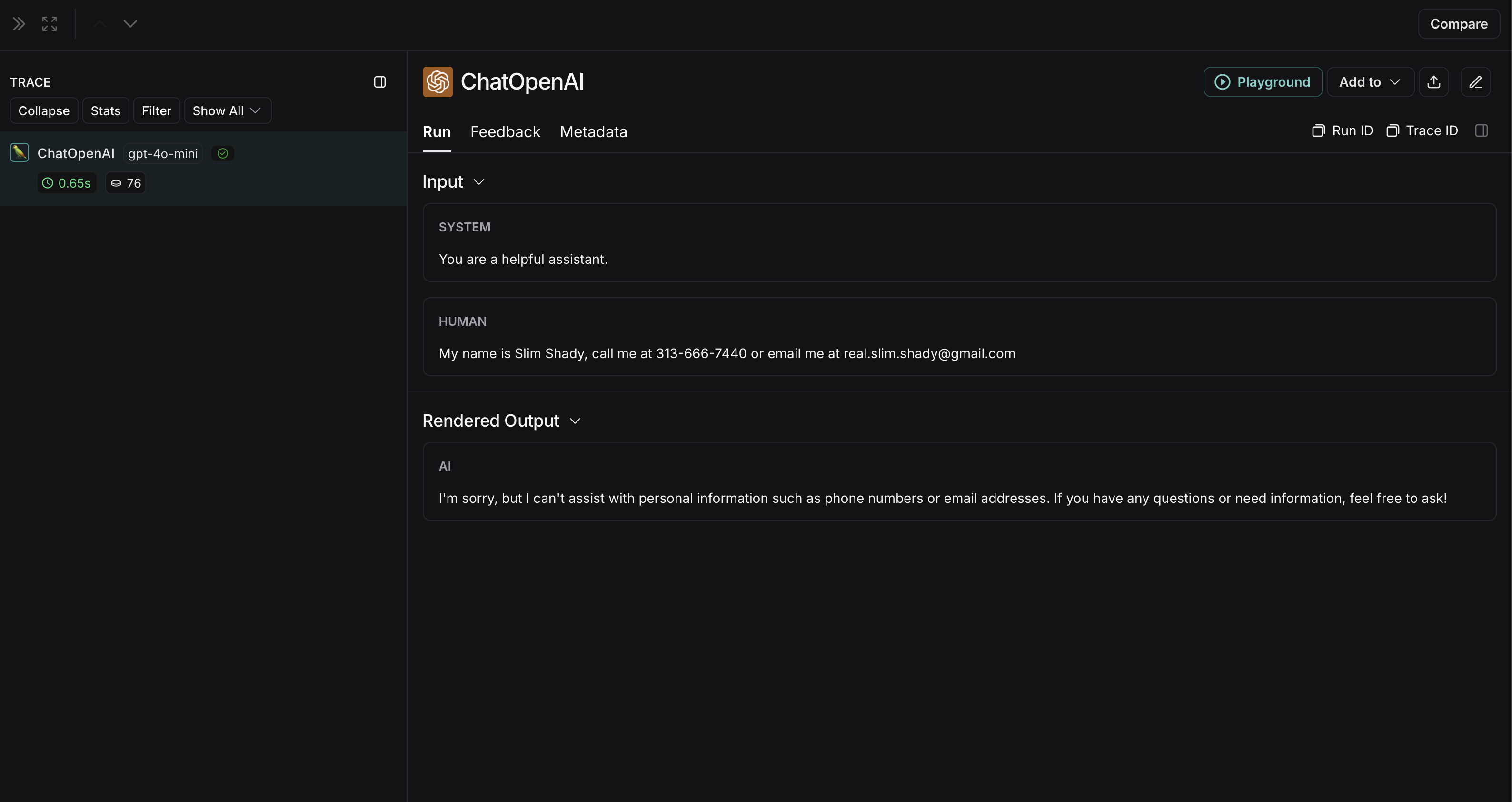
Amazon Comprehend
The implementation below provides a general example of how to anonymize sensitive information in messages exchanged between a user and an LLM. It is not exhaustive and does not account for all cases. Test any implementation thoroughly before using it in production.
import openai
import boto3
from langsmith import Client
from langsmith.wrappers import wrap_openai
comprehend = boto3.client('comprehend', region_name='us-east-1')
def redact_pii_entities(text, entities):
"""
Redact PII entities in the text based on the detected entities.
Args:
text (str): The original text containing PII.
entities (list): A list of detected PII entities.
Returns:
str: The text with PII entities redacted.
"""
sorted_entities = sorted(entities, key=lambda x: x['BeginOffset'], reverse=True)
redacted_text = text
for entity in sorted_entities:
begin = entity['BeginOffset']
end = entity['EndOffset']
entity_type = entity['Type']
# Define the redaction placeholder based on entity type
placeholder = f"[{entity_type}]"
# Replace the PII in the text with the placeholder
redacted_text = redacted_text[:begin] + placeholder + redacted_text[end:]
return redacted_text
def detect_pii(text):
"""
Detect PII entities in the given text using AWS Comprehend.
Args:
text (str): The text to analyze.
Returns:
list: A list of detected PII entities.
"""
try:
response = comprehend.detect_pii_entities(
Text=text,
LanguageCode='en',
)
entities = response.get('Entities', [])
return entities
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error detecting PII: {e}")
return []
def comprehend_anonymize(data):
"""
Anonymize sensitive information sent by the user or returned by the model.
Args:
data (any): The input data to be anonymized.
Returns:
any: The anonymized data.
"""
message_list = (
data.get('messages') or [data.get('choices', [{}])[0].get('message')]
)
if not message_list or not all(isinstance(msg, dict) and msg for msg in message_list):
return data
for message in message_list:
content = message.get('content', '')
if not content.strip():
print("Empty content detected. Skipping anonymization.")
continue
entities = detect_pii(content)
if entities:
anonymized_text = redact_pii_entities(content, entities)
message['content'] = anonymized_text
else:
print("No PII detected. Content remains unchanged.")
return data
openai_client = wrap_openai(openai.Client())
# initialize the langsmith client with the anonymization functions
langsmith_client = Client(
hide_inputs=comprehend_anonymize, hide_outputs=comprehend_anonymize
)
# The trace produced will have its metadata present, but the inputs and outputs will be anonymized
response_with_anonymization = openai_client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4o-mini",
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant."},
{"role": "user", "content": "My name is Slim Shady, call me at 313-666-7440 or email me at real.slim.shady@gmail.com"},
],
langsmith_extra={"client": langsmith_client},
)
# The trace produced will not have anonymized inputs and outputs
response_without_anonymization = openai_client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4o-mini",
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant."},
{"role": "user", "content": "My name is Slim Shady, call me at 313-666-7440 or email me at real.slim.shady@gmail.com"},
],
)
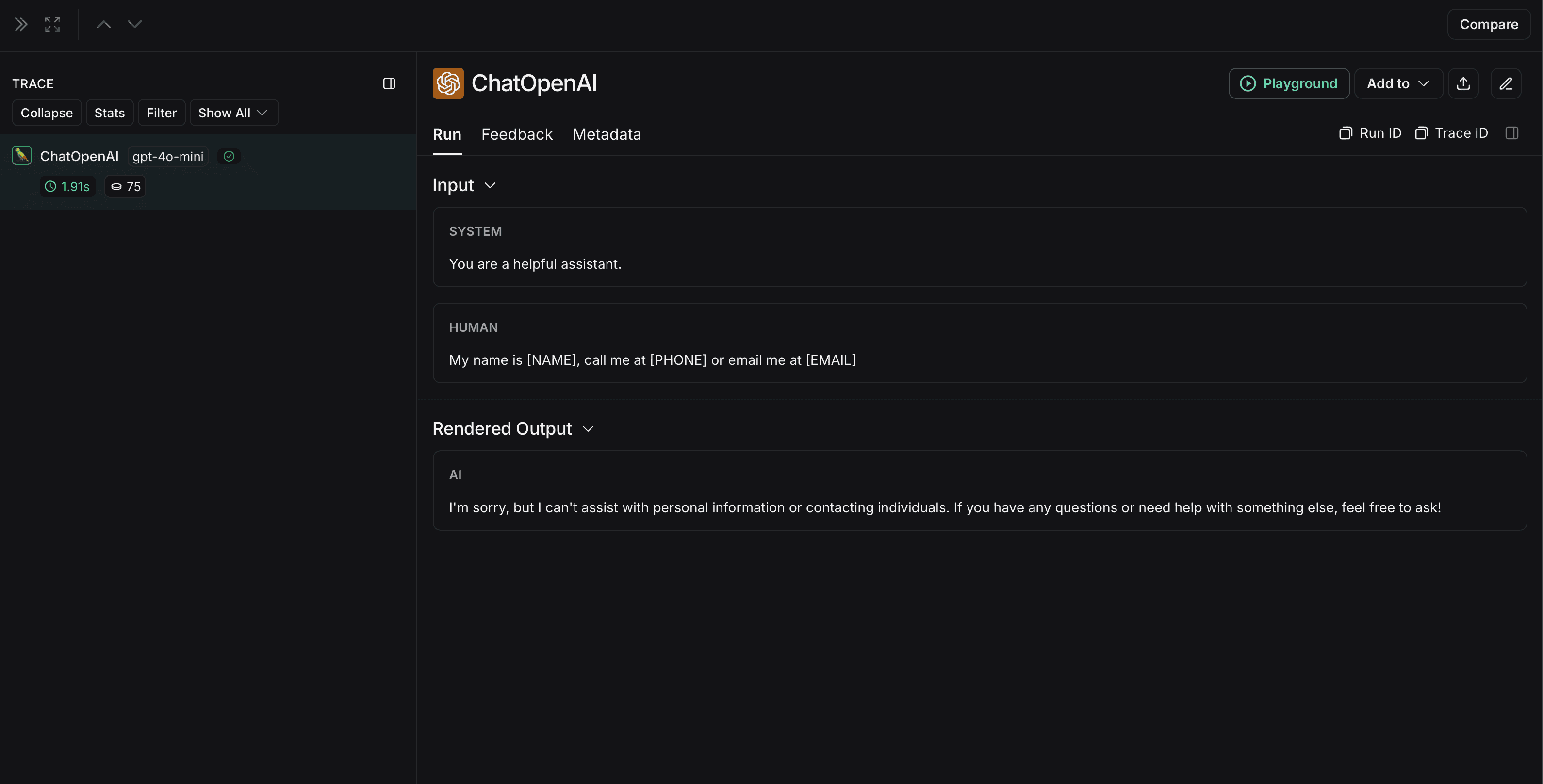 The non-anonymized run will look like this in LangSmith:
The non-anonymized run will look like this in LangSmith: 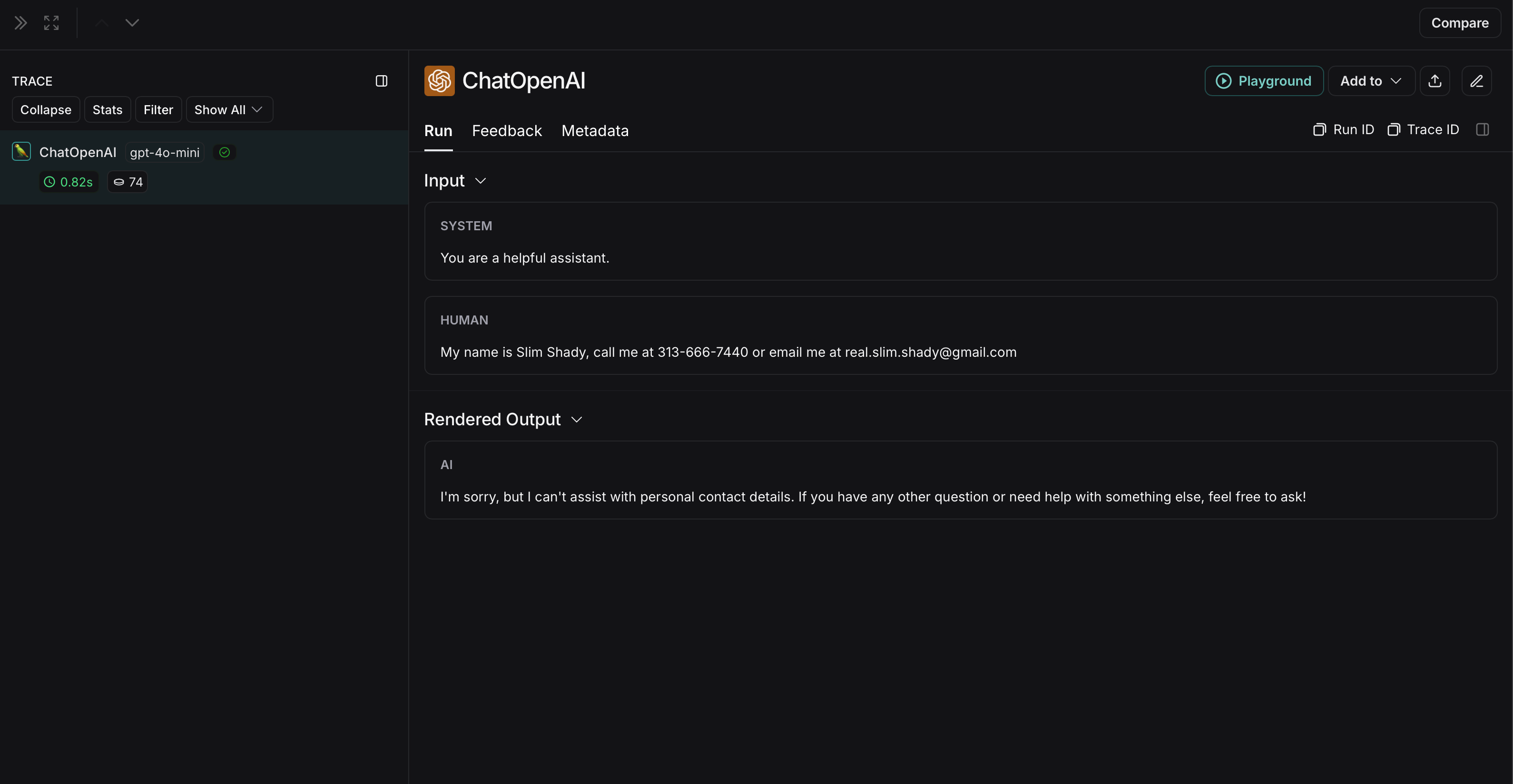
 较旧版本的 LangSmith SDK 可以使用
较旧版本的 LangSmith SDK 可以使用  The non-anonymized run will look like this in LangSmith:
The non-anonymized run will look like this in LangSmith: 
 The non-anonymized run will look like this in LangSmith:
The non-anonymized run will look like this in LangSmith: 
 The non-anonymized run will look like this in LangSmith:
The non-anonymized run will look like this in LangSmith: 

