import os
from typing import List, Dict, Any, Optional
import openai
from langsmith import traceable, Client
import langsmith as ls
from langsmith.wrappers import wrap_openai
# Initialize clients
client = wrap_openai(openai.Client())
langsmith_client = Client()
# Configuration
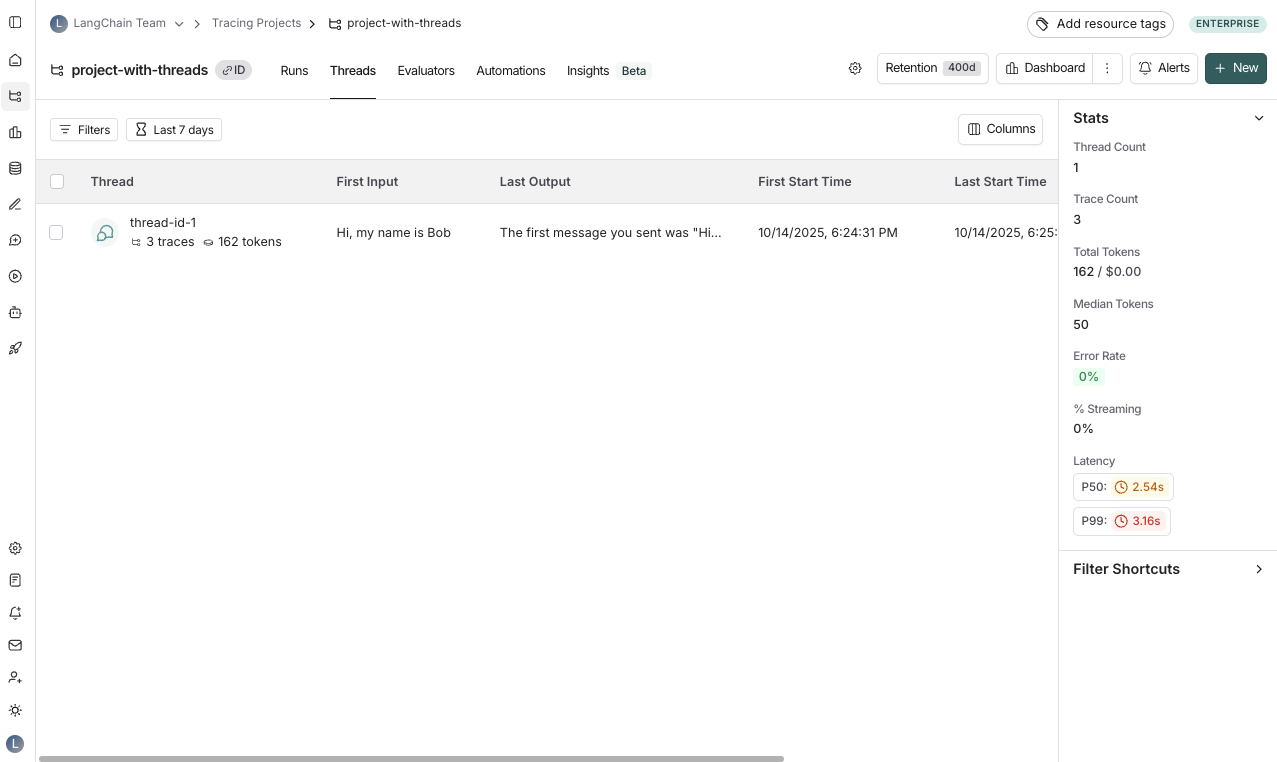
LANGSMITH_PROJECT = "project-with-threads"
THREAD_ID = "thread-id-1"
langsmith_extra={"project_name": LANGSMITH_PROJECT, "metadata":{"session_id": THREAD_ID}}
# gets a history of all LLM calls in the thread to construct conversation history
def get_thread_history(thread_id: str, project_name: str):
# Filter runs by the specific thread and project
filter_string = f'and(in(metadata_key, ["session_id","conversation_id","thread_id"]), eq(metadata_value, "{thread_id}"))'
# Only grab the LLM runs
runs = [r for r in langsmith_client.list_runs(project_name=project_name, filter=filter_string, run_type="llm")]
# Sort by start time to get the most recent interaction
runs = sorted(runs, key=lambda run: run.start_time, reverse=True)
# Reconstruct the conversation state
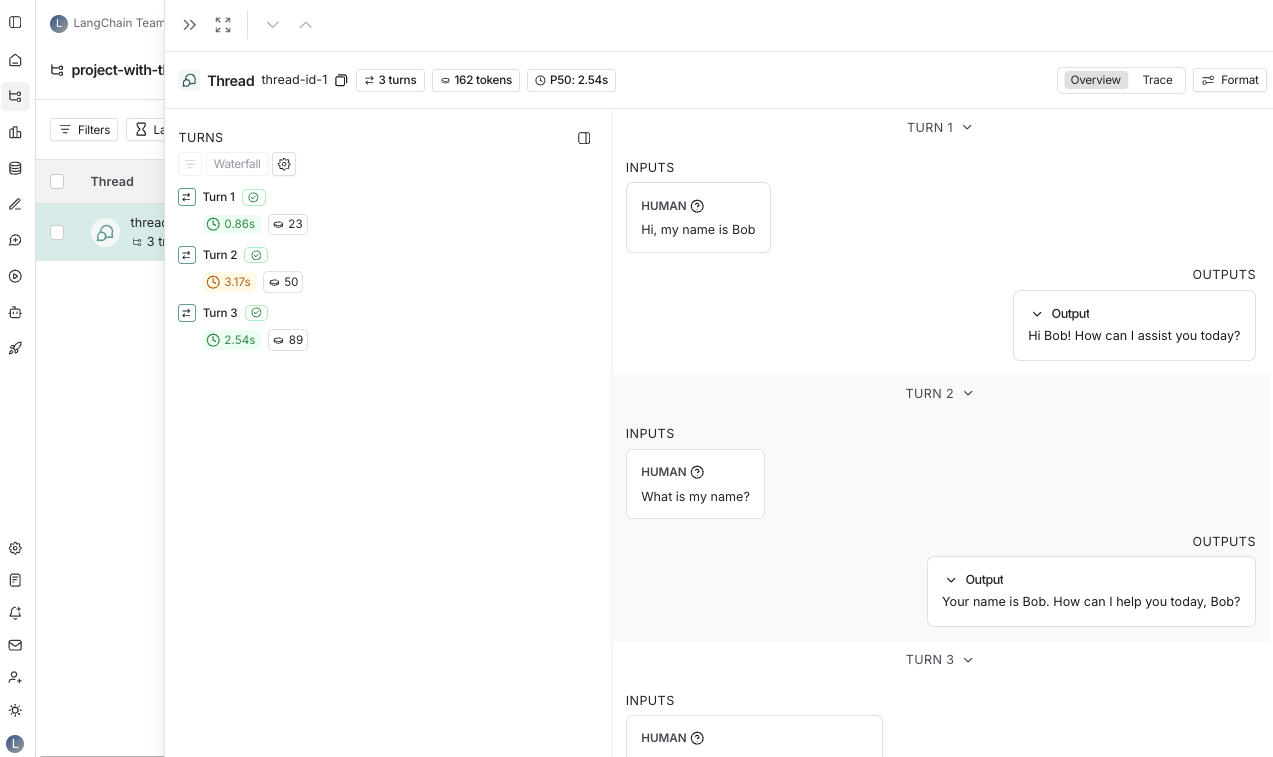
latest_run = runs[0]
return latest_run.inputs['messages'] + [latest_run.outputs['choices'][0]['message']]
@traceable(name="Chat Bot")
def chat_pipeline(messages: list, get_chat_history: bool = False):
# Whether to continue an existing thread or start a new one
if get_chat_history:
run_tree = ls.get_current_run_tree()
# Get existing conversation history and append new messages
history_messages = get_thread_history(run_tree.extra["metadata"]["session_id"], run_tree.session_name)
all_messages = history_messages + messages
# Include the complete conversation in the input for tracing
input_messages = all_messages
else:
all_messages = messages
input_messages = messages
# Invoke the model
chat_completion = client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4o-mini", messages=all_messages
)
# Return the complete conversation including input and response
response_message = chat_completion.choices[0].message
return {
"messages": input_messages + [response_message]
}
# Format message
messages = [
{
"content": "Hi, my name is Sally",
"role": "user"
}
]
get_chat_history = False
# Call the chat pipeline
result = chat_pipeline(messages, get_chat_history, langsmith_extra=langsmith_extra)