- 配置您的环境。
- 创建一个检索上下文并调用 LLM 的应用程序。
- 启用跟踪以捕获检索步骤和 LLM 调用。
- 在 LangSmith UI 中查看生成的跟踪。
先决条件
在开始之前,请确保您具备:- LangSmith 账户:在 smith.langchain.com 注册或登录。
- LangSmith API 密钥:遵循创建 API 密钥指南。
- OpenAI API 密钥:从 OpenAI 仪表板生成。
1. 创建目录并安装依赖项
在终端中,为您的项目创建目录并在环境中安装依赖项:2. 设置环境变量
设置以下环境变量:LANGSMITH_TRACINGLANGSMITH_API_KEYOPENAI_API_KEY(或您的 LLM 提供商的 API 密钥)- (可选)
LANGSMITH_WORKSPACE_ID:如果您的 LangSmith API 密钥链接到多个工作区,请设置此变量以指定要使用的工作区。
3. 定义您的应用程序
您可以使用此步骤中概述的示例应用代码来检测 RAG 应用程序。或者,您可以使用包含 LLM 调用的自己的应用程序代码。 这是一个最小的 RAG 应用,直接使用 OpenAI SDK,尚未添加任何 LangSmith 跟踪。它有三个主要部分:- 检索器函数:模拟文档检索,始终返回相同的字符串。
- OpenAI 客户端:实例化一个普通的 OpenAI 客户端以发送聊天完成请求。
- RAG 函数:将检索到的文档与用户的问题结合起来形成系统提示,使用
gpt-4o-mini调用chat.completions.create()端点,并返回助手的响应。
app.py 或 app.ts):
4. Trace LLM calls
To start, you’ll trace all your OpenAI calls. LangSmith provides wrappers:- Python:
wrap_openai - TypeScript:
wrapOpenAI
-
Include the highlighted lines in your app file:
-
Call your application:
You’ll receive the following output:
- In the LangSmith UI, navigate to the default Tracing Project for your workspace (or the workspace you specified in Step 2). You’ll see the OpenAI call you just instrumented.
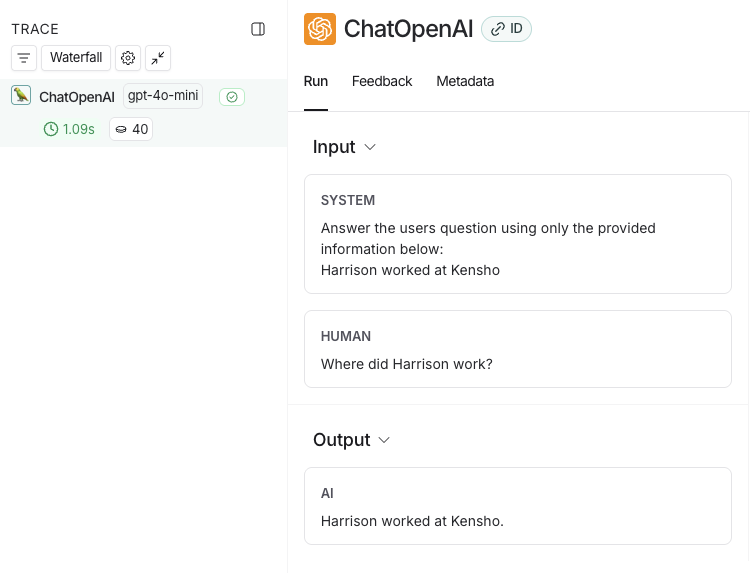
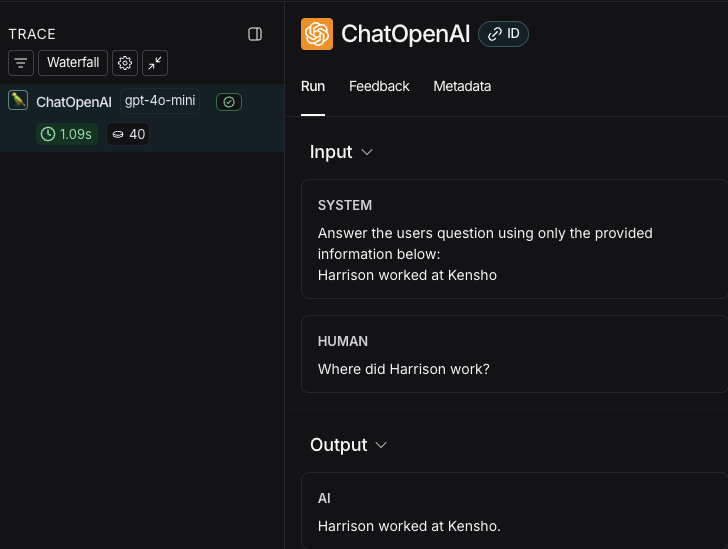
5. Trace an entire application
You can also use thetraceable decorator for Python or TypeScript to trace your entire application instead of just the LLM calls.
-
Include the highlighted code in your app file:
-
Call the application again to create a run:
- Return to the LangSmith UI, navigate to the default Tracing Project for your workspace (or the workspace you specified in Step 2). You’ll find a trace of the entire app pipeline with the rag step and the ChatOpenAI LLM call.


Next steps
Here are some topics you might want to explore next:- Tracing integrations provide support for various LLM providers and agent frameworks.
- Filtering traces can help you effectively navigate and analyze data in tracing projects that contain a significant amount of data.
- Trace a RAG application is a full tutorial, which adds observability to an application from development through to production.
- Sending traces to a specific project changes the destination project of your traces.

