应用部署只是持续改进流程的起点。上线后,你通常需要继续优化提示词、语言模型、工具以及整体架构。回测(Backtesting)指的是利用历史数据评估应用的新版本,并将其输出与原版本对比。相较于仅使用预生产数据集的评估,回测能更直观地反映新版本是否优于当前线上部署。
回测的基本步骤如下:
- 从生产追踪项目中挑选样本运行作为测试对象。
- 将这些运行的输入转成数据集,并把原始输出记录为该数据集的基线实验。
- 使用新系统运行同一数据集,对比实验结果。
通过该流程,你会获得一份具有代表性的输入数据集,可进行版本控制并用于后续模型回测。
在多数情况下,可能无法获取明确的“真值”答案。这时可以人工标注输出,或使用不依赖参考数据的评估器。如果应用允许收集真实标签(例如用户反馈),我们强烈建议启用这类机制。
Setup
安装依赖并设置环境变量。本教程需要 langsmith>=0.2.4。
为方便演示,本文示例使用 LangChain OSS 框架;但所展示的 LangSmith 能力与框架无关。
pip install -U langsmith langchain langchain-anthropic langchainhub emoji
import getpass
import os
# Set the project name to whichever project you'd like to be testing against
project_name = "Tweet Writing Task"
os.environ["LANGSMITH_PROJECT"] = project_name
os.environ["LANGSMITH_TRACING"] = "true"
if not os.environ.get("LANGSMITH_API_KEY"):
os.environ["LANGSMITH_API_KEY"] = getpass.getpass("YOUR API KEY")
# Optional. You can swap OpenAI for any other tool-calling chat model.
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = "YOUR OPENAI API KEY"
# Optional. You can swap Tavily for the free DuckDuckGo search tool if preferred.
# Get Tavily API key: https://tavily.com
os.environ["TAVILY_API_KEY"] = "YOUR TAVILY API KEY"
定义应用
本示例将创建一个简单的推文助手,并为其接入网络搜索工具:
from langchain.chat_models import init_chat_model
from langchain.agents import create_agent
from langchain_community.tools import DuckDuckGoSearchRun, TavilySearchResults
from langchain_core.rate_limiters import InMemoryRateLimiter
# We will use GPT-3.5 Turbo as the baseline and compare against GPT-4o
gpt_3_5_turbo = init_chat_model(
"gpt-3.5-turbo",
temperature=1,
configurable_fields=("model", "model_provider"),
)
# The instrucitons are passed as a system message to the agent
instructions = """You are a tweet writing assistant. Given a topic, do some research and write a relevant and engaging tweet about it.
- Use at least 3 emojis in each tweet
- The tweet should be no longer than 280 characters
- Always use the search tool to gather recent information on the tweet topic
- Write the tweet only based on the search content. Do not rely on your internal knowledge
- When relevant, link to your sources
- Make your tweet as engaging as possible"""
# Define the tools our agent can use
# If you have a higher tiered Tavily API plan you can increase this
rate_limiter = InMemoryRateLimiter(requests_per_second=0.08)
# Use DuckDuckGo if you don't have a Tavily API key:
# tools = [DuckDuckGoSearchRun(rate_limiter=rate_limiter)]
tools = [TavilySearchResults(max_results=5, rate_limiter=rate_limiter)]
agent = create_agent(gpt_3_5_turbo, tools=tools, system_prompt=instructions)
模拟生产数据
下面模拟一批生产环境请求:
fake_production_inputs = [
"Alan turing's early childhood",
"Economic impacts of the European Union",
"Underrated philosophers",
"History of the Roxie theater in San Francisco",
"ELI5: gravitational waves",
"The arguments for and against a parliamentary system",
"Pivotal moments in music history",
"Big ideas in programming languages",
"Big questions in biology",
"The relationship between math and reality",
"What makes someone funny",
]
agent.batch(
[{"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": content}]} for content in fake_production_inputs],
)
将生产追踪转换为实验
第一步是基于生产输入生成数据集,然后复制相应追踪作为基线实验。
选择需要回测的运行
可以通过 list_runs 的 filter 参数挑选回测运行。该参数使用 LangSmith 的追踪查询语法。
from datetime import datetime, timedelta, timezone
from uuid import uuid4
from langsmith import Client
from langsmith.beta import convert_runs_to_test
# Fetch the runs we want to convert to a dataset/experiment
client = Client()
# How we are sampling runs to include in our dataset
end_time = datetime.now(tz=timezone.utc)
start_time = end_time - timedelta(days=1)
run_filter = f'and(gt(start_time, "{start_time.isoformat()}"), lt(end_time, "{end_time.isoformat()}"))'
prod_runs = list(
client.list_runs(
project_name=project_name,
is_root=True,
filter=run_filter,
)
)
将运行转换为实验
convert_runs_to_test 会对运行执行以下操作:
- 将输入(以及可选的输出)保存为数据集示例。
- 将输入与输出写入实验,类似直接调用
evaluate 得到的结果。
# Name of the dataset we want to create
dataset_name = f'{project_name}-backtesting {start_time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d")}-{end_time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d")}'
# Name of the experiment we want to create from the historical runs
baseline_experiment_name = f"prod-baseline-gpt-3.5-turbo-{str(uuid4())[:4]}"
# This converts the runs to a dataset + experiment
convert_runs_to_test(
prod_runs,
# Name of the resulting dataset
dataset_name=dataset_name,
# Whether to include the run outputs as reference/ground truth
include_outputs=False,
# Whether to include the full traces in the resulting experiment
# (default is to just include the root run)
load_child_runs=True,
# Name of the experiment so we can apply evalautors to it after
test_project_name=baseline_experiment_name
)
与新系统对比
现在可以着手将生产运行结果与新系统进行对比。
定义评估器
首先定义用于比较两套系统的评估器。由于没有参考输出,需要设计仅依赖模型实际结果的指标。
import emoji
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field
from langchain_core.messages import convert_to_openai_messages
class Grade(BaseModel):
"""Grade whether a response is supported by some context."""
grounded: bool = Field(..., description="Is the majority of the response supported by the retrieved context?")
grounded_instructions = f"""You have given somebody some contextual information and asked them to write a statement grounded in that context.
Grade whether their response is fully supported by the context you have provided. \
If any meaningful part of their statement is not backed up directly by the context you provided, then their response is not grounded. \
Otherwise it is grounded."""
grounded_model = init_chat_model(model="gpt-4o").with_structured_output(Grade)
def lt_280_chars(outputs: dict) -> bool:
messages = convert_to_openai_messages(outputs["messages"])
return len(messages[-1]['content']) <= 280
def gte_3_emojis(outputs: dict) -> bool:
messages = convert_to_openai_messages(outputs["messages"])
return len(emoji.emoji_list(messages[-1]['content'])) >= 3
async def is_grounded(outputs: dict) -> bool:
context = ""
messages = convert_to_openai_messages(outputs["messages"])
for message in messages:
if message["role"] == "tool":
# Tool message outputs are the results returned from the Tavily/DuckDuckGo tool
context += "\n\n" + message["content"]
tweet = messages[-1]["content"]
user = f"""CONTEXT PROVIDED:
{context}
RESPONSE GIVEN:
{tweet}"""
grade = await grounded_model.ainvoke([
{"role": "system", "content": grounded_instructions},
{"role": "user", "content": user}
])
return grade.grounded
评估基线
现在将评估器运行在基线实验上:
baseline_results = await client.aevaluate(
baseline_experiment_name,
evaluators=[lt_280_chars, gte_3_emojis, is_grounded],
)
# 如果已安装 pandas,可将结果转换为 DataFrame 查看
# baseline_results.to_pandas()
定义并评估新系统
接下来定义并测试新系统。本例中,新系统逻辑与旧版相同,只是将模型从 GPT-3.5 替换为 GPT-4o。由于我们在前面将模型配置暴露出来,只需修改默认配置即可:
candidate_results = await client.aevaluate(
agent.with_config(model="gpt-4o"),
data=dataset_name,
evaluators=[lt_280_chars, gte_3_emojis, is_grounded],
experiment_prefix="candidate-gpt-4o",
)
# 如果已安装 pandas,可将结果转换为 DataFrame 查看
# candidate_results.to_pandas()
对比结果
运行两次实验后,可在数据集中查看对比效果:
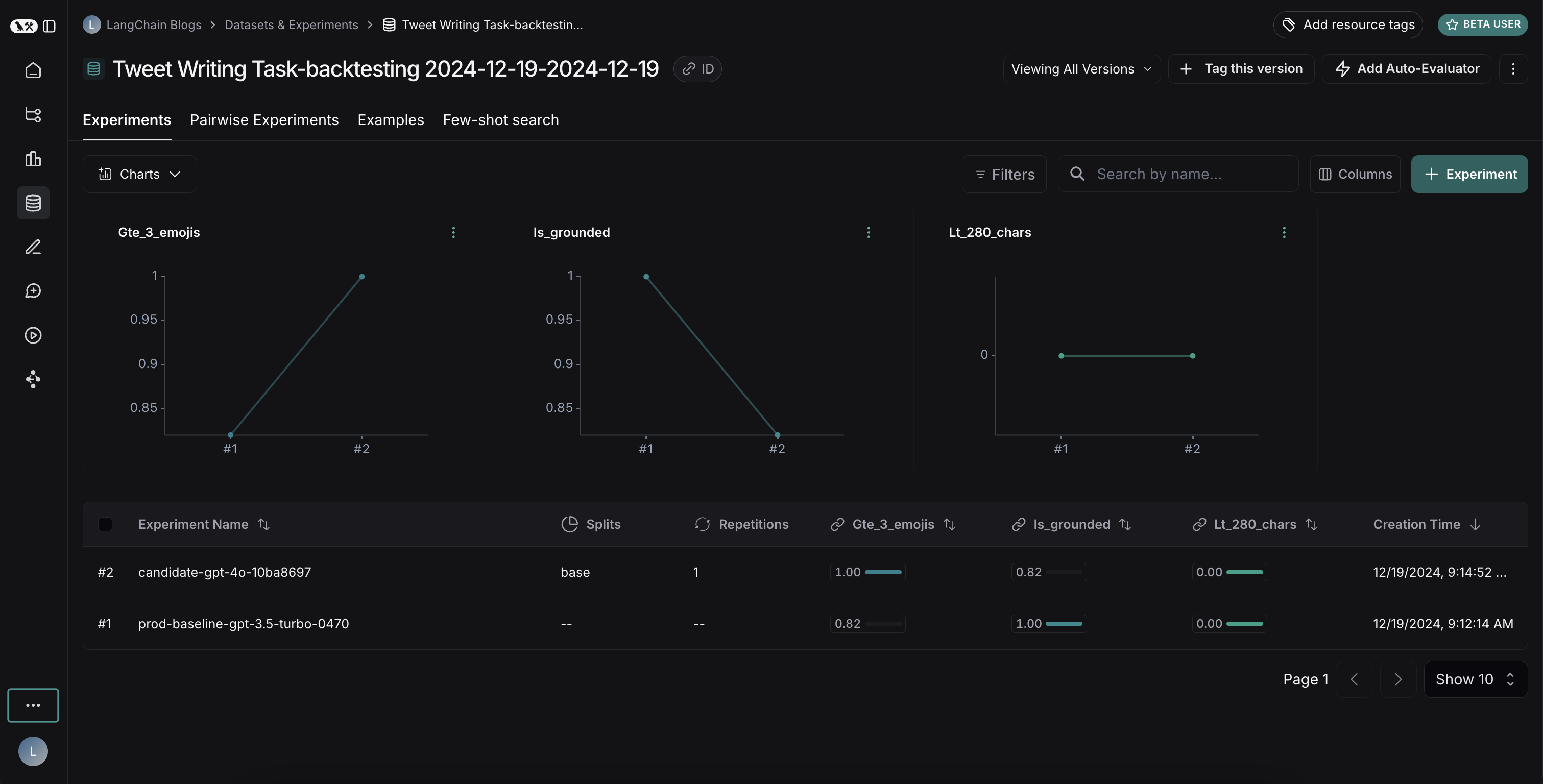 结果揭示了两个模型之间的取舍:
结果揭示了两个模型之间的取舍:
- GPT-4o 在遵守格式规则方面表现更佳,更稳定地输出指定数量的表情
- 但 GPT-4o 更容易脱离搜索结果给出的事实
举例来说,在这条运行记录中,GPT-4o 引入了关于拉齐(Abū Bakr Muhammad ibn Zakariyyā al-Rāzī)医疗贡献的事实,而这些内容并未出现在搜索结果里,说明模型调取了自身知识,而非严格依赖提供的上下文。
回测显示,虽然 GPT-4o 通常被认为能力更强,但直接升级并不会让推文助手变得更好。若要有效使用 GPT-4o,需要:
- 进一步优化提示,强调只使用提供的信息
- 或者调整系统架构,更好地约束模型输出
这也验证了回测的价值——它帮助我们在上线前及时发现潜在问题。


 结果揭示了两个模型之间的取舍:
结果揭示了两个模型之间的取舍:


