为什么需要提示工程?
提示为模型设定舞台,就像即兴表演中的观众成员指导演员的下一次表演 - 它引导模型的行为,而不改变其底层能力。就像告诉演员”成为海盗”决定他们如何表演一样,提示提供指令、示例和上下文,塑造模型的响应方式。 提示工程很重要,因为它允许您更改模型的行为方式。虽然有其他方法可以更改模型的行为(如微调),但提示工程通常是最简单的入门方式,并且通常提供最高的投资回报率。 我们经常看到提示工程是多学科的。有时最好的提示工程师不是构建应用程序的软件工程师,而是产品经理或其他领域专家。拥有适当的工具和基础设施来支持这种跨学科构建很重要。提示 vs. 提示模板
虽然我们经常互换使用这些术语,但理解”提示”和”提示模板”之间的区别很重要。 提示指的是传递到语言模型的消息。 提示模板指的是格式化信息以使该提示保存您想要的信息的方式。提示模板可以包括少样本示例、外部上下文或提示中需要的任何其他外部数据的变量。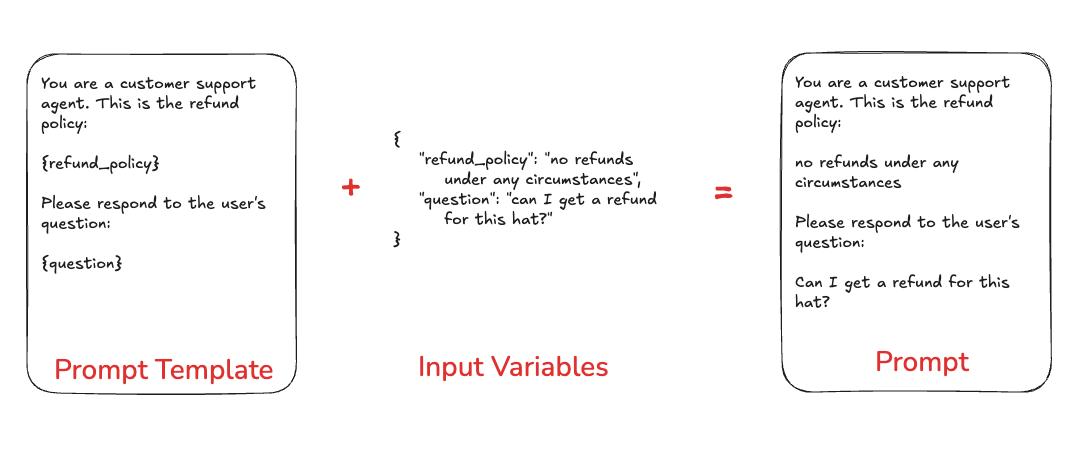
LangSmith 中的提示
您可以在 LangSmith 中存储和版本化提示模板。需要理解提示模板的几个关键方面。聊天 vs 补全
有两种不同类型的提示:chat 风格提示和 completion 风格提示。
聊天风格提示是消息列表。这是当今大多数模型 API 支持的提示风格,因此通常应优先选择。
补全风格提示只是一个字符串。这是一种较旧的提示风格,因此主要出于遗留原因而存在。
F-string vs. mustache
您可以使用 f-string 或 mustache 格式使用输入变量格式化提示。以下是使用 f-string 格式的示例提示:- 游乐场 UI 将获取
is_logged_in变量,但任何嵌套变量您需要自己指定。将以下内容粘贴到输入中以确保上述条件提示有效:
LangSmith 游乐场使用
f-string 作为默认模板格式,但您可以在提示设置/模板格式部分切换到 mustache 格式。mustache 为您提供了围绕条件变量、循环和嵌套键的更大灵活性。对于条件变量,您需要在”输入”部分手动添加 json 变量。阅读文档工具
工具是 LLM 可以用来与外部世界交互的接口。工具包括名称、描述和用于调用工具的参数的 JSON 模式。结构化输出
结构化输出是大多数最先进 LLM 的功能,其中它们不是作为输出生成原始文本,而是坚持指定的模式。这可能会或可能不会在底层使用工具。结构化输出与工具相似,但在几个关键方面有所不同。使用工具时,LLM 选择调用哪个工具(或可能选择不调用任何工具);使用结构化输出时,LLM 始终以此格式响应。使用工具时,LLM 可能选择多个工具;使用结构化输出时,仅生成一个响应。
模型
可选地,您可以将模型配置与提示模板一起存储。这包括模型的名称和任何其他参数(温度等)。提示版本控制
版本控制是迭代和协作不同提示的关键部分。提交
对提示的每次保存的更新都会创建一个具有唯一提交哈希的新提交。这允许您:- 查看提示更改的完整历史记录。
- 查看早期版本。
- 如果需要,恢复到以前的状态。
- 在代码中使用提交哈希引用特定版本(例如,
client.pull_prompt("prompt_name:commit_hash"))。
Tags
Commit tags are human-readable labels that point to specific commits in your prompt’s history. Unlike commit hashes, tags can be moved to point to different commits, allowing you to update which version your code references without changing the code itself. Use cases for commit tags can include:- Environment-specific tags: Mark commits for
productionorstagingenvironments, which allows you to switch between different versions without changing your code. - Version control: Mark stable versions of your prompts, for example,
v1,v2, which lets you reference specific versions in your code and track changes over time. - Collaboration: Mark versions ready for review, which enables you to share specific versions with collaborators and get feedback.
Not to be confused with resource tags: Commit tags reference specific prompt versions. Resource tags are key-value pairs used to organize workspace resources.
Prompt playground
The prompt playground makes the process of iterating and testing your prompts seamless. You can enter the playground from the sidebar or directly from a saved prompt. In the playground you can:- Change the model being used
- Change prompt template being used
- Change the output schema
- Change the tools available
- Enter the input variables to run through the prompt template
- Run the prompt through the model
- Observe the outputs
Testing multiple prompts
You can add more prompts to your playground to easily compare outputs and decide which version is better:
Testing over a dataset
To test over a dataset, you simply select the dataset from the top right and press Start. You can modify whether the results are streamed back as well as how many repitions there are in the test. You can click on the “View Experiment” button to dive deeper into the results of the test.
You can click on the “View Experiment” button to dive deeper into the results of the test.

