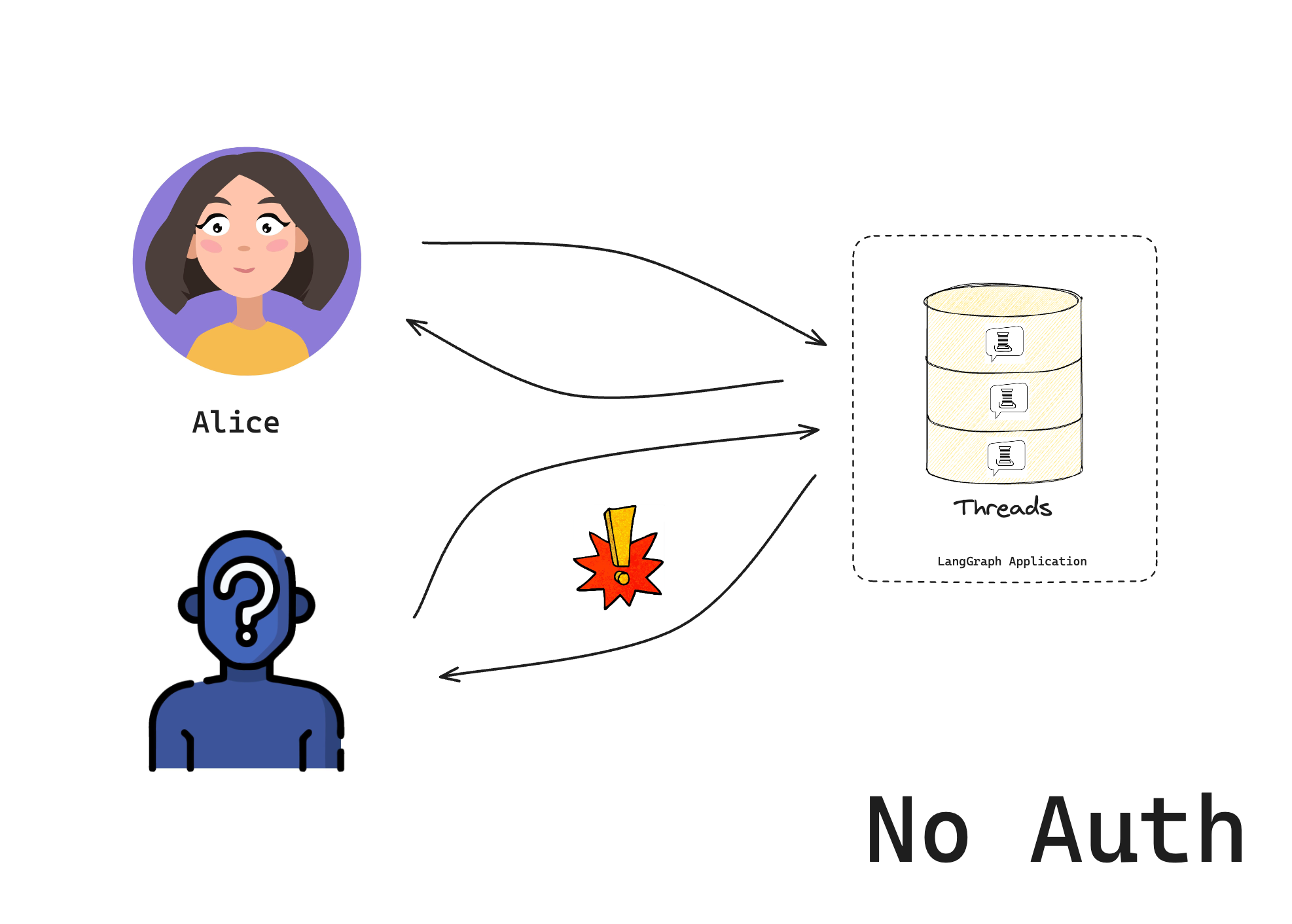
本教程将构建一个仅允许特定用户访问的聊天机器人。我们会从 LangGraph 模板出发,逐步加入基于令牌的安全机制,并最终实现一个会在请求前验证令牌的机器人。
这是身份验证系列的第一篇:
- 自定义身份验证(当前篇)——控制谁能访问你的机器人
- 让对话私有——为用户提供独立的私密会话
- 连接身份验证提供商——接入真实用户账号,使用 OAuth2 做生产级验证
阅读本指南前建议熟悉以下概念:
Custom auth is only available for LangSmith SaaS deployments or Enterprise Self-Hosted deployments.
1. 创建应用
使用 LangGraph 起始模板创建一个新的聊天机器人:
pip install -U "langgraph-cli[inmem]"
langgraph new --template=new-langgraph-project-python custom-auth
cd custom-auth
pip install -e .
langgraph dev
> - 🚀 API: http://127.0.0.1:2024
> - 🎨 Studio UI: https://smith.langchain.com/studio/?baseUrl=http://127.0.0.1:2024
> - 📚 API Docs: http://127.0.0.1:2024/docs
>
> This in-memory server is designed for development and testing.
> For production use, please use LangSmith.
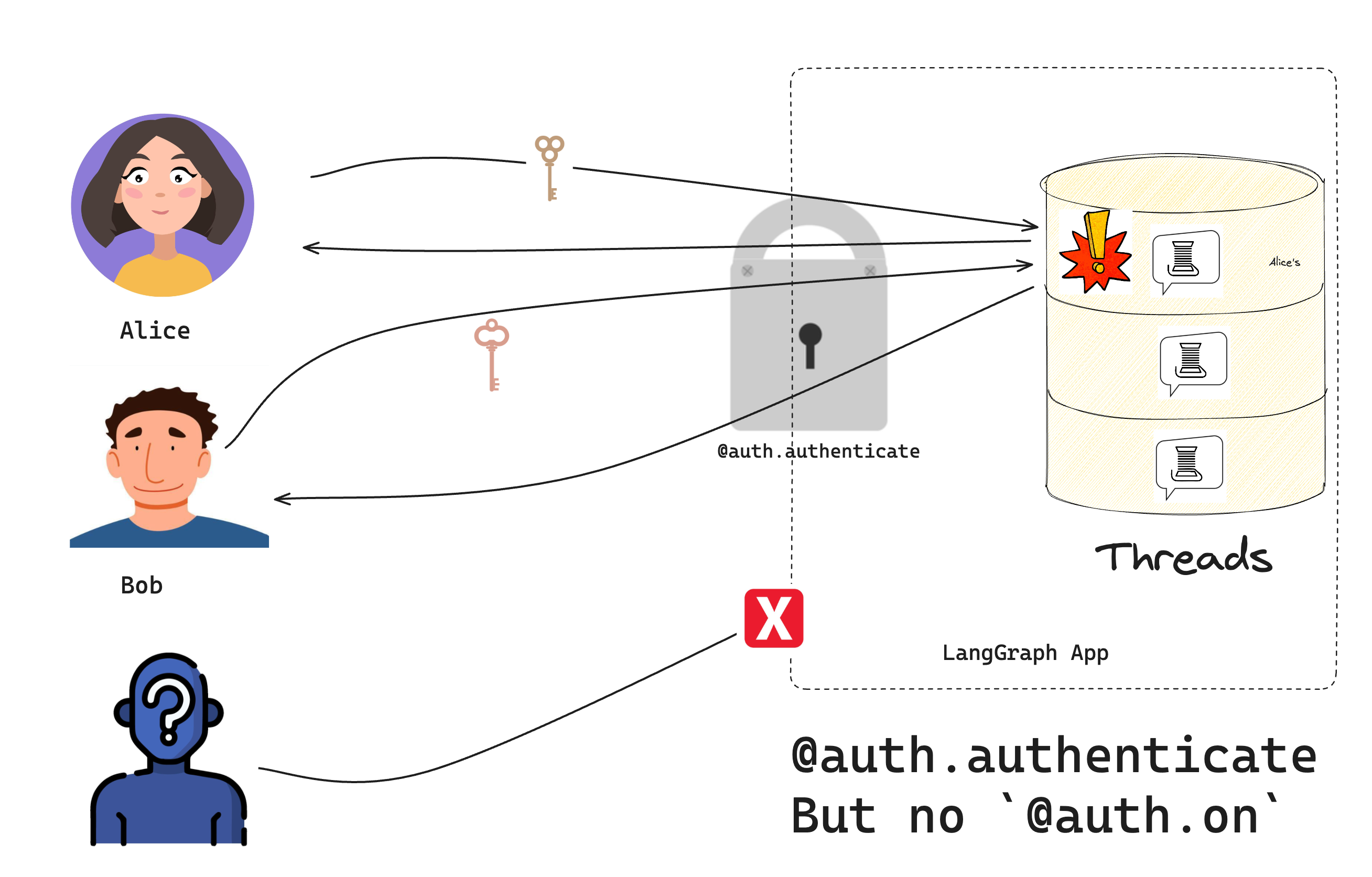
2. 添加身份验证
在已有应用基础上加入身份验证。
本教程先使用硬编码令牌做演示,第三篇会介绍生产就绪的方案。
Auth 对象可注册一个身份验证函数,LangSmith 部署会在每次请求时调用它。该函数负责决定是否允许请求。
新建 src/security/auth.py,用于检查用户是否有权限访问机器人:
from langgraph_sdk import Auth
# This is our toy user database. Do not do this in production
VALID_TOKENS = {
"user1-token": {"id": "user1", "name": "Alice"},
"user2-token": {"id": "user2", "name": "Bob"},
}
# The "Auth" object is a container that LangGraph will use to mark our authentication function
auth = Auth()
# The `authenticate` decorator tells LangGraph to call this function as middleware
# for every request. This will determine whether the request is allowed or not
@auth.authenticate
async def get_current_user(authorization: str | None) -> Auth.types.MinimalUserDict:
"""Check if the user's token is valid."""
assert authorization
scheme, token = authorization.split()
assert scheme.lower() == "bearer"
# Check if token is valid
if token not in VALID_TOKENS:
raise Auth.exceptions.HTTPException(status_code=401, detail="Invalid token")
# Return user info if valid
user_data = VALID_TOKENS[token]
return {
"identity": user_data["id"],
}
- 校验请求的 Authorization 请求头 中是否包含有效令牌
- 返回用户的身份信息
在 langgraph.json 中启用身份验证:
{
"dependencies": ["."],
"graphs": {
"agent": "./src/agent/graph.py:graph"
},
"env": ".env",
"auth": {
"path": "src/security/auth.py:auth"
}
}
3. 测试机器人
重新启动服务器验证配置:
langgraph dev --no-browser
--no-browser,Studio UI 会自动打开。默认情况下,即便启用自定义身份验证,也允许从 Studio 访问,方便开发调试。可在配置中设置 disable_studio_auth: "true" 以移除该备用认证:
{
"auth": {
"path": "src/security/auth.py:auth",
"disable_studio_auth": "true"
}
}
4. 与机器人对话
此时只有在请求头提供有效令牌才能访问机器人。由于尚未添加资源级授权处理器,用户仍可看到彼此资源,这将在后续教程中处理。
 在脚本或 Notebook 中运行以下代码:
在脚本或 Notebook 中运行以下代码:
from langgraph_sdk import get_client
# Try without a token (should fail)
client = get_client(url="http://localhost:2024")
try:
thread = await client.threads.create()
print("❌ Should have failed without token!")
except Exception as e:
print("✅ Correctly blocked access:", e)
# Try with a valid token
client = get_client(
url="http://localhost:2024", headers={"Authorization": "Bearer user1-token"}
)
# Create a thread and chat
thread = await client.threads.create()
print(f"✅ Created thread as Alice: {thread['thread_id']}")
response = await client.runs.create(
thread_id=thread["thread_id"],
assistant_id="agent",
input={"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "Hello!"}]},
)
print("✅ Bot responded:")
print(response)
- 无有效令牌时无法访问机器人
- 有效令牌可正常建线程并对话
恭喜!你已经搭建了一个仅允许“已验证”用户访问的聊天机器人。虽然目前还未达到生产级别的安全性,但已经掌握了控制访问的基础做法。下一篇教程将介绍如何让每位用户拥有自己的私密对话。
后续学习
Now that you can control who accesses your bot, you might want to:
- Continue the tutorial by going to Make conversations private to learn about resource authorization.
- Read more about authentication concepts.
- Check out the API reference for more authentication details.

 在脚本或 Notebook 中运行以下代码:
在脚本或 Notebook 中运行以下代码:

