概述
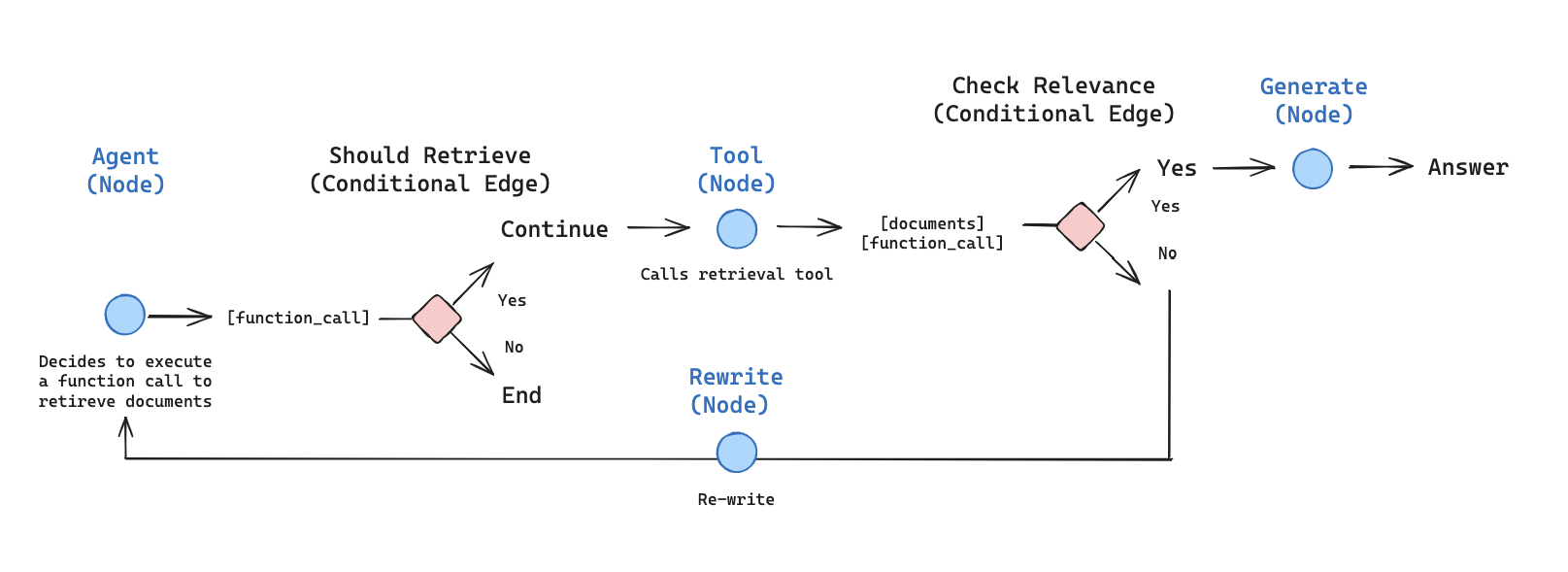
在本教程中,我们将使用 LangGraph 构建一个检索智能体。 LangChain 提供内置的智能体实现,使用 LangGraph 原语实现。如果需要更深入的自定义,可以直接在 LangGraph 中实现智能体。本指南演示了检索智能体的示例实现。当您希望 LLM 决定是从向量存储中检索上下文还是直接响应用户时,检索智能体非常有用。 在本教程结束时,我们将完成以下工作:- 获取和预处理将用于检索的文档。
- 为这些文档建立索引以进行语义搜索,并为智能体创建检索器工具。
- 构建一个可以决定何时使用检索器工具的智能体 RAG 系统。
概念
我们将涵盖以下概念:设置
让我们下载所需的包并设置我们的 API 密钥:Copy
pip install -U langgraph "langchain[openai]" langchain-community langchain-text-splitters bs4
Copy
import getpass
import os
def _set_env(key: str):
if key not in os.environ:
os.environ[key] = getpass.getpass(f"{key}:")
_set_env("OPENAI_API_KEY")
注册 LangSmith 以快速发现问题并提高 LangGraph 项目的性能。LangSmith 让您可以使用跟踪数据来调试、测试和监控使用 LangGraph 构建的 LLM 应用程序。
1. 预处理文档
- 获取要在我们的 RAG 系统中使用的文档。我们将使用 Lilian Weng 优秀博客中最近的三篇文章。我们将首先使用
WebBaseLoader实用程序获取页面内容:
Copy
from langchain_community.document_loaders import WebBaseLoader
urls = [
"https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2024-11-28-reward-hacking/",
"https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2024-07-07-hallucination/",
"https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2024-04-12-diffusion-video/",
]
docs = [WebBaseLoader(url).load() for url in urls]
Copy
docs[0][0].page_content.strip()[:1000]
- 将获取的文档拆分为更小的块以索引到我们的向量存储中:
Copy
from langchain_text_splitters import RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter
docs_list = [item for sublist in docs for item in sublist]
text_splitter = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter.from_tiktoken_encoder(
chunk_size=100, chunk_overlap=50
)
doc_splits = text_splitter.split_documents(docs_list)
Copy
doc_splits[0].page_content.strip()
2. 创建检索器工具
现在我们有了拆分的文档,我们可以将它们索引到向量存储中,用于语义搜索。- 使用内存向量存储和 OpenAI 嵌入:
Copy
from langchain_core.vectorstores import InMemoryVectorStore
from langchain_openai import OpenAIEmbeddings
vectorstore = InMemoryVectorStore.from_documents(
documents=doc_splits, embedding=OpenAIEmbeddings()
)
retriever = vectorstore.as_retriever()
- 使用 LangChain 的预构建
create_retriever_tool创建检索器工具:
Copy
from langchain_classic.tools.retriever import create_retriever_tool
retriever_tool = create_retriever_tool(
retriever,
"retrieve_blog_posts",
"Search and return information about Lilian Weng blog posts.",
)
- 测试工具:
Copy
retriever_tool.invoke({"query": "types of reward hacking"})
3. 生成查询
现在我们将开始为我们的智能 RAG 图构建组件(节点和边)。 请注意,组件将在MessagesState 上操作 — 包含带有聊天消息列表的 messages 键的图状态。
- 构建
generate_query_or_respond节点。它将调用 LLM 根据当前图状态(消息列表)生成响应。给定输入消息,它将决定使用检索器工具进行检索,或直接响应用户。请注意,我们通过.bind_tools让聊天模型访问我们之前创建的retriever_tool:
Copy
from langgraph.graph import MessagesState
from langchain.chat_models import init_chat_model
response_model = init_chat_model("gpt-4o", temperature=0)
def generate_query_or_respond(state: MessagesState):
"""Call the model to generate a response based on the current state. Given
the question, it will decide to retrieve using the retriever tool, or simply respond to the user.
"""
response = (
response_model
.bind_tools([retriever_tool]).invoke(state["messages"])
)
return {"messages": [response]}
- 在随机输入上尝试它:
Copy
input = {"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "hello!"}]}
generate_query_or_respond(input)["messages"][-1].pretty_print()
Copy
================================== Ai Message ==================================
Hello! How can I help you today?
- 提出需要语义搜索的问题:
Copy
input = {
"messages": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": "What does Lilian Weng say about types of reward hacking?",
}
]
}
generate_query_or_respond(input)["messages"][-1].pretty_print()
Copy
================================== Ai Message ==================================
Tool Calls:
retrieve_blog_posts (call_tYQxgfIlnQUDMdtAhdbXNwIM)
Call ID: call_tYQxgfIlnQUDMdtAhdbXNwIM
Args:
query: types of reward hacking
4. 评分文档
- 添加条件边 —
grade_documents— 以确定检索的文档是否与问题相关。我们将使用具有结构化输出模式GradeDocuments的模型进行文档评分。grade_documents函数将根据评分决策返回要去的节点的名称(generate_answer或rewrite_question):
Copy
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field
from typing import Literal
GRADE_PROMPT = (
"You are a grader assessing relevance of a retrieved document to a user question. \n "
"Here is the retrieved document: \n\n {context} \n\n"
"Here is the user question: {question} \n"
"If the document contains keyword(s) or semantic meaning related to the user question, grade it as relevant. \n"
"Give a binary score 'yes' or 'no' score to indicate whether the document is relevant to the question."
)
class GradeDocuments(BaseModel):
"""Grade documents using a binary score for relevance check."""
binary_score: str = Field(
description="Relevance score: 'yes' if relevant, or 'no' if not relevant"
)
grader_model = init_chat_model("gpt-4o", temperature=0)
def grade_documents(
state: MessagesState,
) -> Literal["generate_answer", "rewrite_question"]:
"""Determine whether the retrieved documents are relevant to the question."""
question = state["messages"][0].content
context = state["messages"][-1].content
prompt = GRADE_PROMPT.format(question=question, context=context)
response = (
grader_model
.with_structured_output(GradeDocuments).invoke(
[{"role": "user", "content": prompt}]
)
)
score = response.binary_score
if score == "yes":
return "generate_answer"
else:
return "rewrite_question"
- 使用工具响应中的不相关文档运行此操作:
Copy
from langchain_core.messages import convert_to_messages
input = {
"messages": convert_to_messages(
[
{
"role": "user",
"content": "What does Lilian Weng say about types of reward hacking?",
},
{
"role": "assistant",
"content": "",
"tool_calls": [
{
"id": "1",
"name": "retrieve_blog_posts",
"args": {"query": "types of reward hacking"},
}
],
},
{"role": "tool", "content": "meow", "tool_call_id": "1"},
]
)
}
grade_documents(input)
- 确认相关文档被正确分类:
Copy
input = {
"messages": convert_to_messages(
[
{
"role": "user",
"content": "What does Lilian Weng say about types of reward hacking?",
},
{
"role": "assistant",
"content": "",
"tool_calls": [
{
"id": "1",
"name": "retrieve_blog_posts",
"args": {"query": "types of reward hacking"},
}
],
},
{
"role": "tool",
"content": "reward hacking can be categorized into two types: environment or goal misspecification, and reward tampering",
"tool_call_id": "1",
},
]
)
}
grade_documents(input)
5. Rewrite question
- 构建
rewrite_question节点。检索器工具可能返回可能不相关的文档,这表明需要改进原始用户问题。为此,我们将调用rewrite_question节点:
Copy
REWRITE_PROMPT = (
"Look at the input and try to reason about the underlying semantic intent / meaning.\n"
"Here is the initial question:"
"\n ------- \n"
"{question}"
"\n ------- \n"
"Formulate an improved question:"
)
def rewrite_question(state: MessagesState):
"""Rewrite the original user question."""
messages = state["messages"]
question = messages[0].content
prompt = REWRITE_PROMPT.format(question=question)
response = response_model.invoke([{"role": "user", "content": prompt}])
return {"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": response.content}]}
- 尝试一下:
Copy
input = {
"messages": convert_to_messages(
[
{
"role": "user",
"content": "What does Lilian Weng say about types of reward hacking?",
},
{
"role": "assistant",
"content": "",
"tool_calls": [
{
"id": "1",
"name": "retrieve_blog_posts",
"args": {"query": "types of reward hacking"},
}
],
},
{"role": "tool", "content": "meow", "tool_call_id": "1"},
]
)
}
response = rewrite_question(input)
print(response["messages"][-1]["content"])
Copy
What are the different types of reward hacking described by Lilian Weng, and how does she explain them?
6. Generate an answer
- 构建
generate_answer节点:如果我们通过评分器检查,我们可以根据原始问题和检索的上下文生成最终答案:
Copy
GENERATE_PROMPT = (
"You are an assistant for question-answering tasks. "
"Use the following pieces of retrieved context to answer the question. "
"If you don't know the answer, just say that you don't know. "
"Use three sentences maximum and keep the answer concise.\n"
"Question: {question} \n"
"Context: {context}"
)
def generate_answer(state: MessagesState):
"""Generate an answer."""
question = state["messages"][0].content
context = state["messages"][-1].content
prompt = GENERATE_PROMPT.format(question=question, context=context)
response = response_model.invoke([{"role": "user", "content": prompt}])
return {"messages": [response]}
- 尝试它:
Copy
input = {
"messages": convert_to_messages(
[
{
"role": "user",
"content": "What does Lilian Weng say about types of reward hacking?",
},
{
"role": "assistant",
"content": "",
"tool_calls": [
{
"id": "1",
"name": "retrieve_blog_posts",
"args": {"query": "types of reward hacking"},
}
],
},
{
"role": "tool",
"content": "reward hacking can be categorized into two types: environment or goal misspecification, and reward tampering",
"tool_call_id": "1",
},
]
)
}
response = generate_answer(input)
response["messages"][-1].pretty_print()
Copy
================================== Ai Message ==================================
Lilian Weng categorizes reward hacking into two types: environment or goal misspecification, and reward tampering. She considers reward hacking as a broad concept that includes both of these categories. Reward hacking occurs when an agent exploits flaws or ambiguities in the reward function to achieve high rewards without performing the intended behaviors.
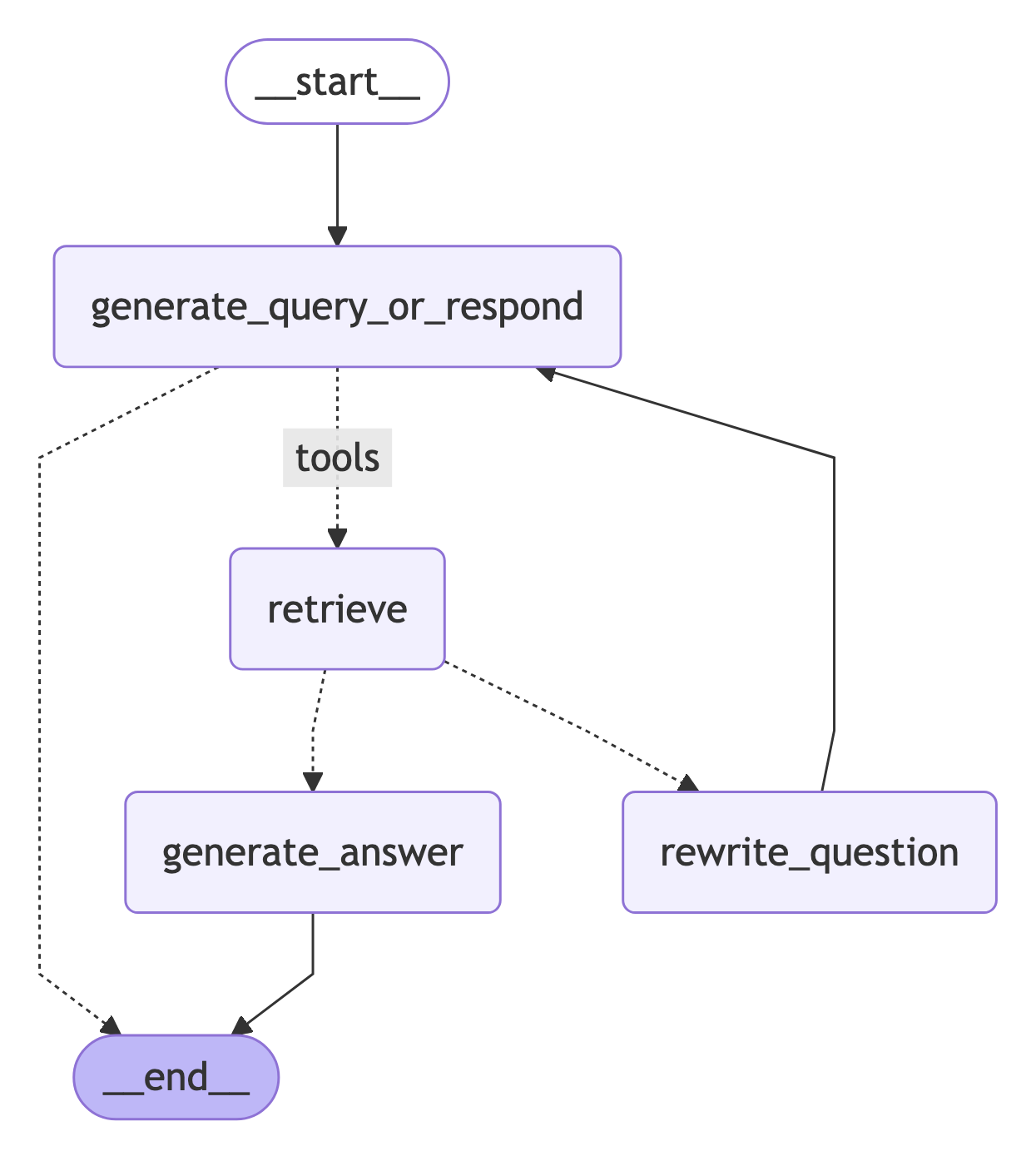
7. Assemble the graph
现在我们将把所有节点和边组装成一个完整的图:- 从
generate_query_or_respond开始并确定是否需要调用retriever_tool - 使用
tools_condition路由到下一步:- 如果
generate_query_or_respond返回tool_calls,调用retriever_tool检索上下文 - 否则,直接响应用户
- 如果
- 为问题的相关性对检索的文档内容进行评分(
grade_documents)并路由到下一步:- 如果不相关,使用
rewrite_question重写问题,然后再次调用generate_query_or_respond - 如果相关,继续到
generate_answer并使用带有检索的文档上下文的ToolMessage生成最终响应
- 如果不相关,使用
Copy
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph, START, END
from langgraph.prebuilt import ToolNode, tools_condition
workflow = StateGraph(MessagesState)
# 定义我们将在其间循环的节点
workflow.add_node(generate_query_or_respond)
workflow.add_node("retrieve", ToolNode([retriever_tool]))
workflow.add_node(rewrite_question)
workflow.add_node(generate_answer)
workflow.add_edge(START, "generate_query_or_respond")
# 决定是否检索
workflow.add_conditional_edges(
"generate_query_or_respond",
# 评估 LLM 决策(调用 `retriever_tool` 工具或响应用户)
tools_condition,
{
# 将条件输出转换为图中的节点
"tools": "retrieve",
END: END,
},
)
# 调用 `action` 节点后采取的边
workflow.add_conditional_edges(
"retrieve",
# 评估智能体决策
grade_documents,
)
workflow.add_edge("generate_answer", END)
workflow.add_edge("rewrite_question", "generate_query_or_respond")
# 编译
graph = workflow.compile()
Copy
from IPython.display import Image, display
display(Image(graph.get_graph().draw_mermaid_png()))
8. Run the agentic RAG
现在让我们通过使用问题运行来测试完整的图:Copy
for chunk in graph.stream(
{
"messages": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": "What does Lilian Weng say about types of reward hacking?",
}
]
}
):
for node, update in chunk.items():
print("Update from node", node)
update["messages"][-1].pretty_print()
print("\n\n")
Copy
Update from node generate_query_or_respond
================================== Ai Message ==================================
Tool Calls:
retrieve_blog_posts (call_NYu2vq4km9nNNEFqJwefWKu1)
Call ID: call_NYu2vq4km9nNNEFqJwefWKu1
Args:
query: types of reward hacking
Update from node retrieve
================================= Tool Message ==================================
Name: retrieve_blog_posts
(Note: Some work defines reward tampering as a distinct category of misalignment behavior from reward hacking. But I consider reward hacking as a broader concept here.)
At a high level, reward hacking can be categorized into two types: environment or goal misspecification, and reward tampering.
Why does Reward Hacking Exist?#
Pan et al. (2022) investigated reward hacking as a function of agent capabilities, including (1) model size, (2) action space resolution, (3) observation space noise, and (4) training time. They also proposed a taxonomy of three types of misspecified proxy rewards:
Let's Define Reward Hacking#
Reward shaping in RL is challenging. Reward hacking occurs when an RL agent exploits flaws or ambiguities in the reward function to obtain high rewards without genuinely learning the intended behaviors or completing the task as designed. In recent years, several related concepts have been proposed, all referring to some form of reward hacking:
Update from node generate_answer
================================== Ai Message ==================================
Lilian Weng categorizes reward hacking into two types: environment or goal misspecification, and reward tampering. She considers reward hacking as a broad concept that includes both of these categories. Reward hacking occurs when an agent exploits flaws or ambiguities in the reward function to achieve high rewards without performing the intended behaviors.
Connect these docs programmatically to Claude, VSCode, and more via MCP for real-time answers.

